Health
Opposition Leader has advice for TCIG now that Delta variant landed
Published
4 years agoon

#TurksandCaicos, August 20, 2021 –
We should Be Concerned about the Delta Variant
After a year and a half, we are still in the pandemic. It is the survival of the fittest between humans and the coronavirus Variants. We are racing to herd immunity, to get more people vaccinated and to get more effective antiviral medications.
We are seeing people dismiss COVID as a just another common cold, and even worse not wearing masks in public places or social distancing. We are also seeing a lack of compliance to the established COVID-19 protocols. We are seeing most safety protocols being abandoned and persons going back to business as usual pre-COVID. We are seeing persons, some who are vaccinated, travelling to cities with high rates of new COVID-19 cases and returning back home to the Turks and Caicos Islands without knowing their COVID status.
With new cases now emerging daily in the TCI the situation could deteriorate very rapidly. We should not allow the flood gates to be wide open. We as a country cannot ease up our efforts at this time, and should not stop fighting until the virus has been defeated. We have to do whatever it takes to battle this unseen enemy.
Therefore, we should be very concerned about the newer, faster transmitting, Delta Variant (B16172). This Variant seems to be the prevalent strain circulating in the TCI at the moment, and has been seen to be two times more infectious than the original G-Variant. Recent reports from the UK indicate that the Delta Variant is infecting younger people more than the original variant, and that the symptoms are different.
With the original variant infected persons would present with symptoms of high fever, muscle pains, cough, severe chest pain etc., but with the Delta Variant, many infected persons are presenting with symptoms of stuffy or running nose, sneezing, sore throat, and mild headaches. Younger people usually show little or no symptoms, and are less likely to get tested, hence not knowing their COVID status and possible spreading the virus more.
Additionally, scientific data sources are now showing that vaccinated persons with a good immune system may also become infected and show little or mild symptoms, and not get tested, and possibly spread the virus to susceptible individuals. 
Viruses have one goal, that is to make more copies of themselves (to multiply), and since they can’t do it on their own, they use us (a host). They infect our body cells and use them to make copies of themselves. They replicate themselves many times, making millions of copies of themselves, but eventually it makes a mistake. The mistake is referred to as a mutation, and it changes the instructions for making the virus. That slightly altered virus is a Variant. Mutations in viruses happen all the time, producing new variants. Most of the time these mutations are insignificant or make the virus weaker, and they naturally disappear. But sometimes a series of mutations makes the virus stronger, and gives it an edge over its host. These advantages include giving the viruses the ability to bind to the human cells better, and the ability to enter the cells easier, making the virus more transmissible, allowing it to become the dominant strain in many places around the world.
It is important to remember that mutations are random errors, but the longer a virus is around, and the more people it infects, the more it will change, and the more those changes accumulate, the more chance the virus has to evolve into a more dangerous variant.
The Delta Variant which is the most recent addition to this list of dangerous Variants, is described as a “Double Mutant”, whose mutations seems to make it more transmissible, as it binds to the cell receptors better than other variants, thus blocking those other variants from binding. Its mutations also made it more easy to infect people who have had COVID-19. This means this Variant has a greater change to evade our body’s natural immune response.
Scientific Data has shown that the immune response we get from vaccines are stronger than what we get from a natural response to the virus. Therefore, we would see some persons who previously contracted COVID-19 becoming re-infected, and there would be persons who have taken the vaccine becoming infected with COVID-19 (breakthrough cases). But the difference being seen is that the effect on vaccinated individuals is less severe with possibly no symptoms and are less likely to be admitted to the hospital.
The virus has evolved, and will continue to produce variants, some which may give it an advantage. So if we want to prevent the possibility of a deadlier, and more transmissible strain from developing, we need to stop the Virus.
The Pandemic is not over, even if it feels that way to some of us. The virus has mutated to become more transmissible. Now is not the time for the Turks and Caicos, nor the rest of the world to let its guard down.
The Delta Variant is now presenting as the prevalent variant in a number of countries, and certainly it is now present in the Turks & Caicos. The more we test the more we pick up on silent cases in our communities.
We are now better equipped to respond to the pandemic, and our ability to test is now so much better. Our hospital capacity is now much better to deal with COVID patients, including the availability of oxygen generation.
The New PNP Government must now do its part and insure that our Health Care System stays adequately staffed with the necessary health professionals to care for our hospitalized individuals, and that the right complement of health workers is employed to respond to Outbreaks and Pandemics, that is, having trained staff to perform Surveillance and Monitoring activities, Compliance activities, Testing and research, quarantining, vaccinating, community work, and School Health.
Additionally, the new PNP Government needs to make the tough, and sometimes unpopular decision to ensure that the right policies and guidelines are put in place for the mitigation of further spread of Variants, and for protecting our country and our people.
We should never just focus on what we are seeing today, but must always try to keep a few steps ahead of the virus, by looking at what future advances and abilities are needed. The Government should be looking at what are the technologies and enhancements we could make based on the lessons we have learned, and making the containment, monitoring, and reduction in spread of COVID Variant, and other new viruses much better the next time around.
Hon. Edwin A. Astwood
Leader of the Opposition
You may like
-

Startling News: Turks and Caicos Records July COVID-19 Death as Regular Tracking Resumes & global cases up 11%
-


Opposition Leader Meets with Governor, Calls for National Strategy to Curb Gun Violence
-


Statement from the Leader of the Opposition on the Recent Tragedy in Providenciales
-


TCI Ministry of Health Monitoring SARS-CoV-2 Variant NB.1.8.1 and Reminds Public of Preventive Measures
-


TCI Health Officials on Alert as COVID Variant Emerges and Cases Rise in Key Travel Destinations
-


Two Realities, One Country: Opposition Leader Slams Government’s ‘Disconnected’ $540M Budget
Health
Bruce Willis’ Brave Gift to Dementia Research – And His now Quiet Link to Turks & Caicos
Published
2 months agoon
December 4, 2025
December 4, 2025 – Hollywood legend Bruce Willis – arguably the most famous former home owner in Turks and Caicos Islands – is facing the most difficult role of his life and turning it into one last act of service.
Willis, 70, retired from acting in 2022 after his family revealed he had been diagnosed with aphasia. The following year, specialists confirmed he is living with frontotemporal dementia (FTD), a degenerative brain disease that attacks language, behaviour and personality.
confirmed he is living with frontotemporal dementia (FTD), a degenerative brain disease that attacks language, behaviour and personality.
In recent interviews and appearances, his wife Emma Heming Willis has said Bruce is “surrounded by love and care” and that the family is learning to find joy in new ways, even as the disease progresses.
Now, Heming Willis has gone further. In her 2025 memoir The Unexpected Journey, she writes that the family has decided Bruce’s brain will be donated to science after his death to advance research into FTD. That decision has been highlighted in recent coverage by futurist and science outlets, which describe it as a carefully considered step after months of watching a still-physically-strong man steadily lose speech, reading and independence.
Neurologists have long stressed how rare donated brain tissue is for FTD, and how essential it is to understanding which proteins, mutations and mechanisms are actually driving the disease. The Willis family’s choice means the brain that powered some of cinema’s most iconic characters could one day help researchers diagnose the condition earlier and design better treatments – even if it cannot help Bruce himself.
For Turks and Caicos, the story lands close to home. For nearly two decades Willis owned “The Residence” on exclusive Parrot Cay – a 7.3-acre, Asian-inspired beachfront compound with a five-bedroom main house, two guest villas and a yoga pavilion. He and Emma listed the estate in March 2019 for US$33 million; it sold a few months later for about US$27 million, one of the biggest residential deals in TCI history.
So, while Bruce Willis no longer has a physical address in Turks and Caicos, his connection to these islands remains part of his global story – a story now shifting from blockbuster fame to medical legacy, as his family turns private heartbreak into a public contribution that could change what we know about dementia.
Developed by Deandrea Hamilton • with ChatGPT (AI) • edited by Magnetic Media.
Health
From 54 New Cases in July to Zero in August: TCI’s COVID Turnaround
Published
5 months agoon
September 6, 2025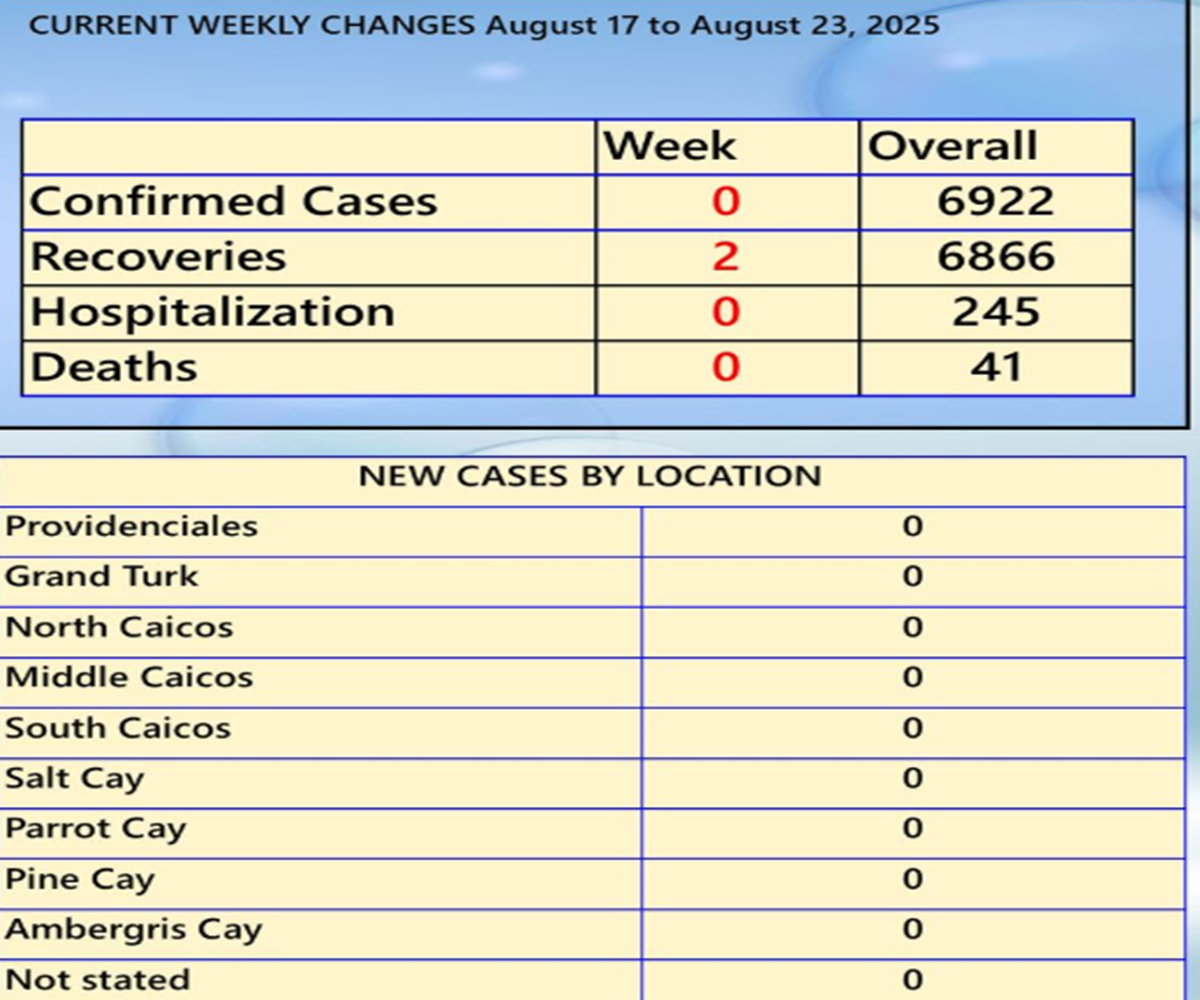
Deandrea Hamilton | Editor
Turks and Caicos, September 6, 2025 – COVID-19 fears in the Turks and Caicos Islands that once had residents on edge are now giving way to a sense of relief. The Ministry of Health and Human Services reports a dramatic reversal: from dozens of new cases in July to zero cases and zero hospitalizations today.
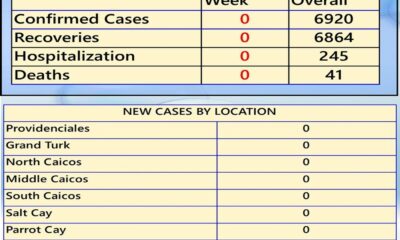
Between August 17 and 23, 2025, officials confirmed no new cases, no hospitalizations, and no new deaths. Just two recoveries were recorded, bringing the national recovery tally to 6,866. The total confirmed cases since 2020 stand at 6,922, with deaths unchanged at 41. Health officials say August has been relatively quiet overall, with 19 new cases and recoveries recorded for the month — a fraction of what the islands faced just weeks earlier.
The contrast could not be sharper. The most concerning bulletin came in mid-July, when the Ministry reported 54 new cases in a single week. Ten were fresh positives, while the other 44 came from a backlog of April samples. At that time, two new hospitalizations were recorded, and the islands mourned one additional COVID-related death, bringing the total to 41. It was a sobering reminder that the virus was still circulating, pushing recoveries to 6,845 and raising the cumulative case count to 6,910. The July spike stirred fear among residents and renewed calls for vigilance, as community spread and delayed lab results painted a worrying picture.
week. Ten were fresh positives, while the other 44 came from a backlog of April samples. At that time, two new hospitalizations were recorded, and the islands mourned one additional COVID-related death, bringing the total to 41. It was a sobering reminder that the virus was still circulating, pushing recoveries to 6,845 and raising the cumulative case count to 6,910. The July spike stirred fear among residents and renewed calls for vigilance, as community spread and delayed lab results painted a worrying picture.
Fast forward to late August, and the numbers tell a very different story. Not only are new cases negligible, but the hospitals are reporting no COVID-19 patients at all. Officials say testing continues across a wide range of categories, and the Ministry urges the public to stay cautious: wash hands, wear masks in crowded spaces, protect the vulnerable, and get vaccinated. But the tone now is one of optimism.
Since the pandemic began in 2020, Turks and Caicos has recorded nearly 7,000 cases in total, with 6,866 recoveries and 41 deaths. The islands’ small population means every case has felt significant, and surges like July’s were especially unsettling. But today’s figures suggest the country has reached a new stage: COVID-19 is no longer the disruptive force it was. The Ministry credits continued public vigilance and the accessibility of free testing and vaccines at government clinics. While the numbers are cause for celebration, health leaders are careful not to declare the fight over. The Ministry’s latest bulletin reminds residents to maintain hygienic practices, follow self-isolation guidelines if infected, and ensure vaccinations are up to date.
The pandemic may not be entirely behind the Turks and Caicos, but compared to the frightening figures of July, the near-zero landscape of August offers a powerful sign of hope.
The Ministry released the bulletin on September 2, confirming that for the week of August 17–23, no new cases, hospitalizations, or deaths were recorded — a sharp contrast to the surge just weeks earlier.
Health
Turks and Caicos Islands Health Delegation Completes Strategic Visits to Florida and Cayman Islands to Advance Health Sector Reform and Strengthen Treatment Abroad Programme
Published
5 months agoon
August 29, 2025
Providenciales, Turks and Caicos Islands, 22 August 2025 — A high-level delegation from the Ministry of Health and Human Services (MOHHS) has successfully concluded strategic working visits to Florida and the Cayman Islands from August 5–13, 2025. The mission aimed to strengthen the Treatment Abroad Programme, explore innovative health system models, and advance the Turks and Caicos Islands’ health sector reform agenda through strategic regional partnerships.
Delegation Members:
- Hon. Kyle Knowles – Minister of Health and Human Services
- Mrs. Desiree Lewis – Permanent Secretary, Health and Human Services
- Mr. Lynrod Brooks – Director, Health Policy and Planning
- Ms. Florinda Talbot – Contract Performance Manager
- Mrs. Romaine Missick-Smith – CEO, Health Regulations Authority
- Ms. Jasmine Malcolm – Executive Administrator, MOHHS
Minister of Health and Human Services, Hon. Kyle Knowles, highlighted the significance of these engagements:
“These visits were not ceremonial; they were strategic, focused, and impactful. In Florida, we reinforced partnerships with leading healthcare providers to ensure TCI patients referred overseas receive the highest standards of clinical care and patient support. In the Cayman Islands, our mission was two-fold: to study the operations of the Cayman Islands Health Services Authority as a model to guide the establishment of our own Health Services Authority, and to strengthen ties with Cayman-based treatment partners, where many of our patients are referred under the Treatment Abroad Programme. Both visits underscored that small island states share many health challenges, and that collaboration, innovation, and adapting best practices to our local context are essential to achieving better health outcomes for our people.”
Florida – Strengthening the Treatment Abroad Programme
During the period August 5–9, the delegation visited Broward Medical Center, University of Miami Health System, Cleveland Clinic, Nicklaus Children’s Hospital, and the International Reinsurance Managers Network. They also toured REVA Air Ambulance Services to review medical evacuation operations and patient transfer management. Discussions centered on patient care pathways, specialized services in ophthalmology, cardiology, oncology, and pediatrics, family-centered care models, advanced telemedicine for pre- and post-treatment consultations, and reinsurance strategies for high-cost overseas cases. Key outcomes include agreements to expand telehealth consultations, develop a standardized referral package to reduce delays, explore reinsurance arrangements to safeguard public health budgets, and establish specialized pediatric transfer protocols.
Cayman Islands – Health Sector Reform and Treatment Abroad Partnerships
From August 10–13, the delegation engaged with senior executives at Health City Cayman Islands, including Dr. Binoy Chattuparambil (Clinical Director), Shomari Scott (Chief Business Development Officer), Rebecca Brooks (Head of Marketing and Sales), and Ingrid Harris (Sales and Marketing). The team toured two hospital facilities and held in-depth discussions with Lizzette Yearwood, Chief Executive Officer along with leadership staff of the Cayman Islands Health Services Authority
The focus was two-fold:
- Health Sector Reform – Examining governance, financial management, and operational structures of the Cayman Islands HSA model
to inform TCI’s development of its own Health Services Authority.
- Treatment Abroad Strengthening – Reviewing current referral arrangements with Cayman healthcare partners to enhance patient care coordination and improve treatment pathways for TCI patients referred to Cayman.
The delegation also met with Honourable Katherine Ebanks-Wilks, Minister for Health, Environment, Sustainability, and Honourable G. Wayne Panton, Parliamentary Secretary for Health. The team concluded with a meeting with Acting Premier Hon. Gary B. Rutty and Cabinet members, reaffirming the shared commitment to improving healthcare access and outcomes through regional collaboration.
Next Steps
The Ministry will incorporate lessons learned from these visits into ongoing health reform planning, ensuring that the proposed Health Services Authority is tailored to TCI’s needs while reflecting regional best practices. Efforts will continue to ensure that the Treatment Abroad Programme delivers efficient, sustainable, and patient-centered care.








