A week of wind, water, and heartbreak
From Haiti’s hillsides to Bermuda’s reefs, seven Caribbean nations have been battered, bruised, and forever marked by Hurricane Melissa — a storm that tested not only the region’s infrastructure but its unshakable spirit of unity.
Saturday–Sunday, October 25–26 – The First Strike: Hispaniola
Before the storm even earned its name, torrential rain and flash floods swept across Haiti and the Dominican Republic, claiming lives and tearing through rural communities.
tearing through rural communities.
In southern Haiti, rivers burst their banks, swallowing roads and homes; 23 people were confirmed dead by Sunday evening. Across the border, one death was reported in the Dominican Republic as swollen rivers cut off villages in Barahona and Pedernales.
By nightfall, the tropical system had strengthened — and the Caribbean knew it was facing something historic.
Monday, October 27 – Evacuations and Airlifts
In The Bahamas, Prime Minister Philip Davis issued a mandatory evacuation for the MICAL Islands — Mayaguana, Inagua, Crooked Island, Acklins, Long Cay, and Ragged Island.
Bahamasair added extra flights as the nation braced for what forecasters warned could become the strongest storm in nearly two decades.
Meanwhile, Jamaica, Turks & Caicos, and Cuba activated their national emergency operations centers.
Tuesday, October 28 – Jamaica and Haiti Hit Hard
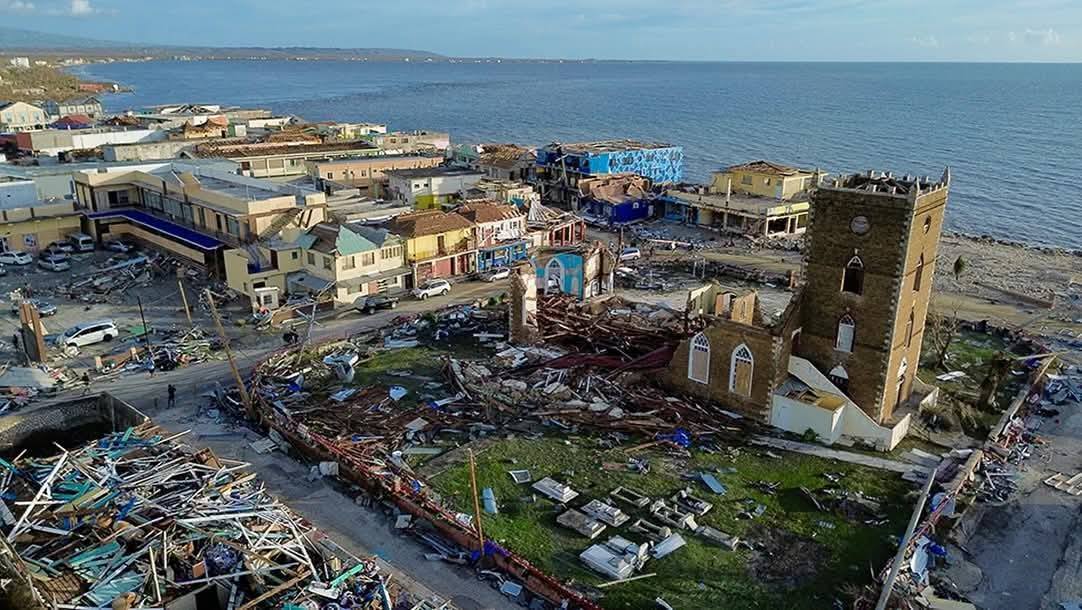
By afternoon, Hurricane Melissa made landfall near St Elizabeth, Jamaica, as a Category 5 hurricane — winds of 185 mph, central pressure 892 mb, the lowest ever recorded so close to the island.
Roads collapsed, bridges washed away, and Black River Hospital lost its roof. Power failed for 72 percent of the island.
BOJ TV footage shows split asphalt, sparking lines, and flooded communities abandoned for safety.
Initially four were reported dead, that grew to seven deaths and heavy damage in 170 communities; Andrew Holness, Jamaican Prime Minister calling it “a national test of resilience.”
Haiti, still recovering from the weekend’s flooding, was hit again as outer bands dumped more rain on Les Cayes and Jacmel, deepening the humanitarian crisis.
Wednesday, October 29 – Crossing to Cuba
Weakened slightly to Category 4 (145 mph), Melissa tracked north-northeast at 8 mph, hammering eastern Cuba with hurricane-force winds

and mudslides. Over 15 000 people were evacuated from Santiago de Cuba and Holguín.
In Turks & Caicos, the Regiment deployed to Grand Turk, Salt Cay, South, North and Middle Caicos, preparing shelters and securing public buildings.
Thursday, October 30 – The Bahamas and the All Clear
Melissa’s speed increased, sparing the northern Caribbean its worst.
The Bahamas Airport Authority closed 13 airports from Mayaguana to Exuma International; none reported casualties, though infrastructure suffered.
In Turks & Caicos, the all-clear came early Thursday after minimal impact. Premier Washington Misick expressed gratitude and pledged support for neighbors:
“We must act — not only with words, but with compassion and deeds.”
Friday, October 31 – Counting the Cost
By Friday, Melissa had weakened to Category 3 (120 mph) north of Cuba.
The Bahamas Department of Meteorology issued its final alert, lifting warnings for the southern islands.
Regional toll:
- Haiti: 23 dead, thousands displaced.
- Jamaica: 7 dead, 170 communities damaged; 72% without electricity
- Cuba: 2 dead, 15, 000 evacuated.
- Dominican Republic: 1 dead, flooding in southwest.
- Bahamas: 0 dead, minor infrastructure damage and flooding in southeast.
- Turks & Caicos: minimal to no impact.
Relief and Reconnection
The Cayman Islands became the first government to touch down in Jamaica post-storm. Premier Juliana O’Connor-Connolly led a contingent bringing a plane-load of essentials and pledged US $1.2 million in aid.
Reggae icon Shaggy arrived on a private jet with friends, delivering food, medical kits, and hygiene supplies.
Meanwhile, Starlink and FLOW Jamaica activated emergency satellite internet across Jamaica providing free connectivity through November.
From overseas, U.S. President Donald Trump, speaking during his Asia tour, announced that American search-and-rescue teams and disaster aid will support the region.
“They can depend on U.S. assistance as they recover from this historic storm,” he said.
Faith, Funds, and False Websites
The Government of Jamaica and the Sandals Foundation have both launched verified donation portals for recovery. Officials are warning against fake crowdfunding pages posing as relief sites and urging donors to use only official channels.
A Seventh Nation in the Crosshairs – Bermuda
As Hurricane Melissa left the Caribbean basin, Bermuda found itself next in line.
Forecasts indicated the storm would pass just west of the island late Thursday into Friday, likely as a Category 1 to 2 hurricane with sustained winds near 105 mph.
Though far weaker than when it ravaged Jamaica, officials issued a hurricane warning, urging residents to secure property and expect tropical-storm conditions.
By all appearances Bermuda is heeding the warnings
The Human Response
Across the Caribbean, solidarity surged.
The Global Empowerment Mission (GEM) in Miami began airlifting relief supplies, while churches, civic groups, and businesses in The Bahamas and Turks & Caicos organized drives for displaced families.
“Your dedication gave our islands the strength to face the storm,” Premier Misick said. “Together, as one Caribbean family, we will rise stronger.”
Resilience in the Wake
Melissa’s winds may have faded, but her impact endures. Engineers are inspecting bridges, hillsides, and water systems; volunteers are clearing debris and distributing aid in communities still cut off.
From Haiti’s ravaged river valleys to Jamaica’s sugar towns, from Cuba’s eastern hills to The Bahamas’ salt ponds and Bermuda’s reefs, the region once again stands at the crossroads of ruin and renewal — and leans, as always, toward hope and a faithful God


 world news1 week ago
world news1 week ago
 TCI News1 week ago
TCI News1 week ago
 TCI News1 week ago
TCI News1 week ago
 TCI News1 week ago
TCI News1 week ago
 Uncategorized1 week ago
Uncategorized1 week ago
 USA1 week ago
USA1 week ago
 TCI News1 week ago
TCI News1 week ago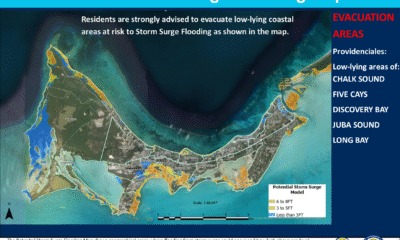
 TCI News4 days ago
TCI News4 days ago


























