Health
Breakthrough in Maternal care to save mothers & babies

Health
Dengue cases rising in Region
Health
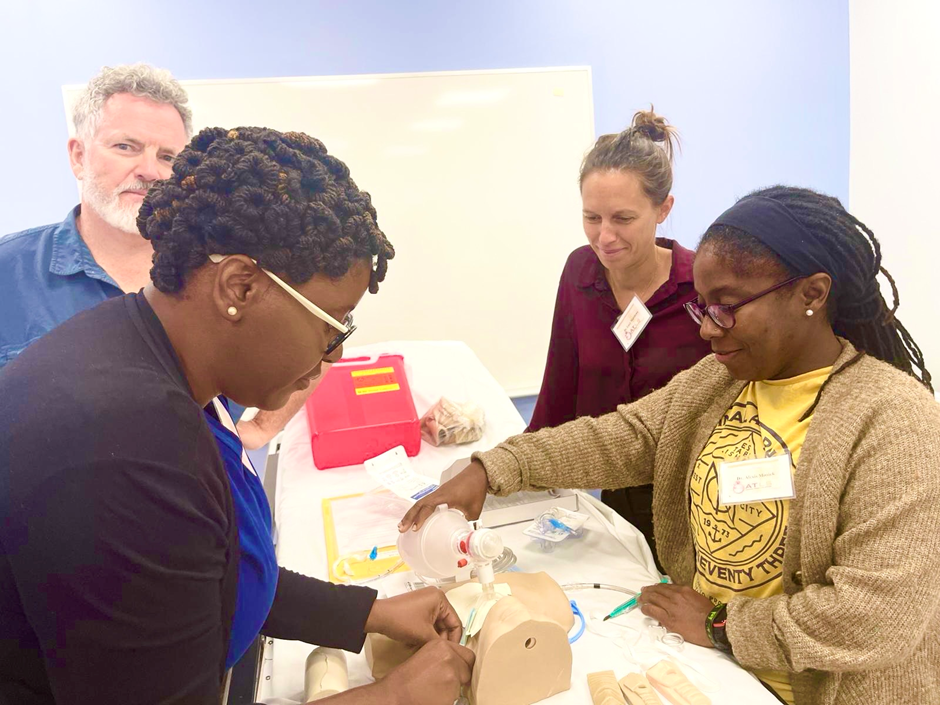
31 Turks & Caicos Medical Professionals, Trained in Trauma care
Caribbean News
Dengue surges in Argentina; Repellent shortage reported
-

 Caribbean News1 week ago
Caribbean News1 week agoBarbados welcomes new aircraft
-

 Caribbean News1 week ago
Caribbean News1 week agoHaiti political update and Trinidad and Tobago not sending troops for mission
-
 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoDengue passes 1000 deaths mark in Brazil
-

 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoTURKS AND CAICOS ISLANDS PARTICIPATED IN EIGHTH MEETING OF NATIONAL HIV/AIDS PROGRAMME MANAGERS AND PANCAP SHARE FAIR
-

 Caribbean News5 days ago
Caribbean News5 days agoHaiti Gang Firearms more than Police – UN says where they come from.
-

 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoChildren and Teens Vaping, Royal TCI Police say “IT IS NOT SAFE!”
-

 Caribbean News5 days ago
Caribbean News5 days agoGuyana Wildfires
-

 Caribbean News2 days ago
Caribbean News2 days agoCARICOM, UN applauds published decree establishing Haiti’s Transitional Government