Health
ChikV is back! The Americas see sharp increase and nearly 100 deaths

Caribbean News
CARPHA Provides Technical Support for Malaria Intervention in Turks and Caicos Islands
Caribbean News
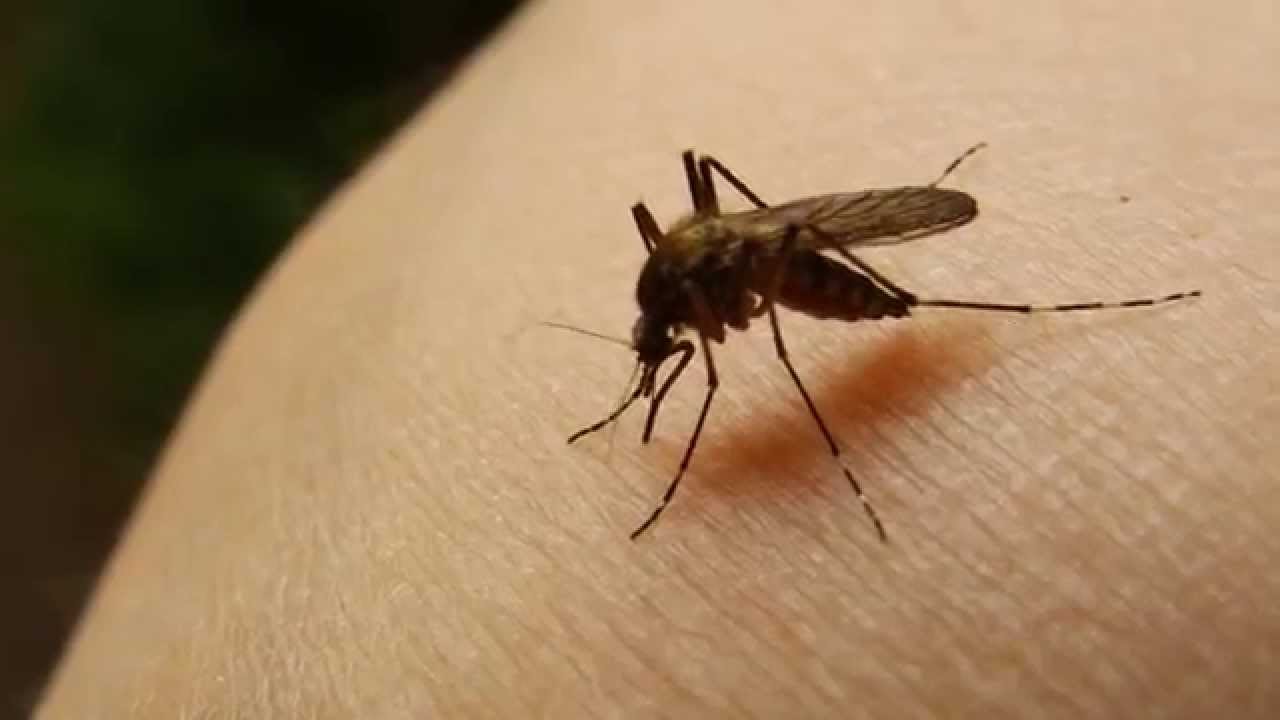
CARPHA Calls on Member States to Take Action to Reduce the Spread of Mosquito Borne Diseases
Caribbean News
From Awareness to Action: Public Health Matters
-

 Caribbean News7 days ago
Caribbean News7 days agoCayman Relief Mission to Hurricane hit CARICOM nations
-

 Caribbean News7 days ago
Caribbean News7 days agoCARICOM raising profile and priority of its Migration Policy; curbing challenges ‘a tall order’
-

 Caribbean News1 week ago
Caribbean News1 week agoHurricane Help; Money donated to Jamaica, Barbados, St Vincent & the Grenadines, St Lucia and Grenada
-

 Caribbean News7 days ago
Caribbean News7 days agoJamaica’s Hurricane Recovery Efforts Bolstered by Donation from Cayman Islands
-

 Bahamas News7 days ago
Bahamas News7 days agoPrime Minister Davis: Cannabis Reform Compendium 2024 ‘a long time coming’
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoWhat the new UK Prime Minister had to say about the Rwanda Deportation Plan at his first press conference
-

 Bahamas News1 week ago
Bahamas News1 week agoBahamas Celebrates 51st Independence – ‘United In Love & Service’
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoTurks & Caicos’ E.J Saunders part of Election Observer team in UK on July 4