By Deandrea Hamilton
Editor
November 29, 2022 – It’s a 52-year-old name which has run its course and in a year will be completely phased out, making way for its new, more politically correct and patient sensitive title: MPox. The World Health Organization briefed the world of the shift in a media statement on Monday November 29; the renaming process described as “accelerated.”
“When the outbreak of monkeypox expanded earlier this year, racist and stigmatizing language online, in other settings and in some communities was observed and reported to WHO. In several meetings, public and private, a number of individuals and countries raised concerns and asked WHO to propose a way forward to change the name.”
The World Health Organization has as part of its global health remit, to name or rename illnesses in consultation with its member states; some 45 countries weighed in on this particular change which factored in stigmatization and versatility.
“Various advisory bodies were heard during the consultation process, including experts from the medical and scientific and classification and statistics advisory committees which constituted of representatives from government authorities of 45 different countries.
The issue of the use of the new name in different languages was extensively discussed. The preferred term mpox can be used in other languages. If additional naming issues arise, these will be addressed via the same mechanism. Translations are usually discussed in formal collaboration with relevant government authorities and the related scientific societies.”
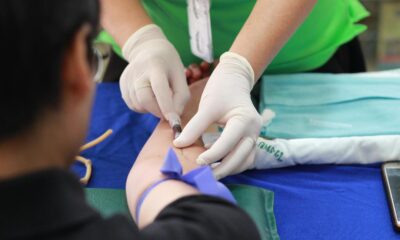
Although monkeyPox symptoms disappear on their own in a matter of weeks, for some the symptoms have led to medical complications and death. Immuno-compromised children are listed as particularly vulnerable, so are newborn babies.
“Complications from monkeypox include secondary skin infections, pneumonia, confusion, and eye problems. More recent complications include proctitis (sores and swelling inside the rectum that cause pain) and pain or difficulty when urinating. In the past, between 1% to 10% of people with monkeypox have died. It is important to note that death rates in different settings may differ due to a number of factors, such as access to health care. These figures may be an overestimate because surveillance for monkeypox has generally been limited in the past,” informed the CDCs website.
recent complications include proctitis (sores and swelling inside the rectum that cause pain) and pain or difficulty when urinating. In the past, between 1% to 10% of people with monkeypox have died. It is important to note that death rates in different settings may differ due to a number of factors, such as access to health care. These figures may be an overestimate because surveillance for monkeypox has generally been limited in the past,” informed the CDCs website.
Dr Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, Direcgtor-General, WHO in considering the advice from health experts specifically recommends: “Adoption of the new synonym mpox in English for the disease; Mpox will become a preferred term, replacing monkeypox, after a transition period of one year. This serves to mitigate the concerns raised by experts about confusion caused by a name change in the midst of a global outbreak. It also gives time to complete the ICD update process and to update WHO publications; The synonym mpox will be included in the ICD-10 online in the coming days. It will be a part of the official 2023 release of ICD-11, which is the current global standard for health data, clinical documentation and statistical aggregation. The term “monkeypox” will remain a searchable term in ICD, to match historic information.”
As of November 28, there had been 81,188 cases of mpox recorded worldwide according to the US Centers for Disease Control (CDC). Most alarming; over 80,000 of the cases have been recorded in locations not historically known to have monkeypox. Some 110 countries have now recorded mpox, a staggering 103 of them are newly added to the list of nations where the disease has been detected.
The biggest explosion of cases is recorded in the United States; 29,288 people were confirmed with the disease and 14 people have died as a result of it.
Regionally, Cuba, Dominican Republic, Jamaica, The Bahamas, Aruba, Curacao, Barbados, Martinique, Guadeloupe, Bermuda and Guyana have confirmed mpox on their shores.
In the coming days, the new mpox name will be added to the International Classification of Diseases or ICD and will be used in communication from health bodies. While the label: MonkeyPox will become a relic, it will continue to be used for at least another year.
“WHO will adopt the term mpox in its communications, and encourages others to follow these recommendations, to minimize any ongoing negative impact of the current name and from adoption of the new name,” it said in the statement posted at its website.
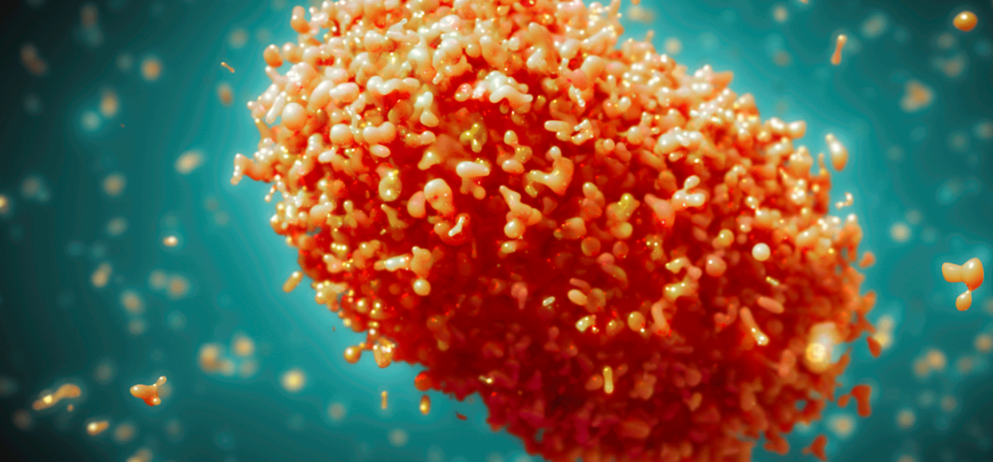
Photo credit:
Maurizio de Angelis/Science photo library
Monkeypox virus, illustration. Monkeypox virus particles are composed of a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) genome surrounded by a protein coat and lipid envelope.

 Caribbean News7 days ago
Caribbean News7 days ago
 Caribbean News7 days ago
Caribbean News7 days ago
 Caribbean News1 week ago
Caribbean News1 week ago
 Caribbean News7 days ago
Caribbean News7 days ago
 Bahamas News7 days ago
Bahamas News7 days ago
 News7 days ago
News7 days ago
 Bahamas News1 week ago
Bahamas News1 week ago
 News7 days ago
News7 days ago